Configure Sophos Firewall to use DNS Protection
If you're using Sophos Firewall as the DNS server, you can configure the firewall to use DNS Protection as the DNS forwarder. To do this, you must add the DNS Protection IP addresses to the firewall.
To configure Sophos Firewall, do as follows:
- In Sophos Central, go to My Products > DNS Protection > Installers.
-
Next to IP addresses, click Copy to copy the DNS Protection IP addresses.
You copy two IP addresses. You can use them as the primary and secondary DNS Protection IP addresses to configure redundancy.
-
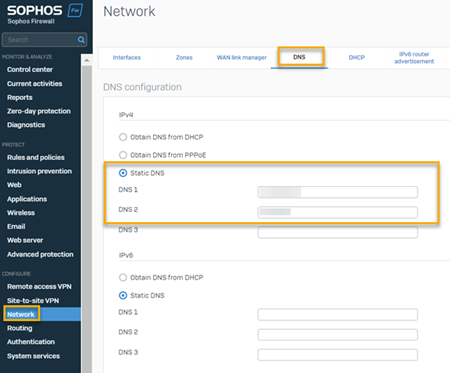
In Sophos Firewall, go to Network > DNS.
- Select Static DNS.
- In DNS 1, enter the IP address you want to use as the primary DNS Protection Server. This must be one of the addresses you copied from Sophos Central.
-
In DNS 2, enter the IP address you want to use as the secondary DNS Protection server. This must be one of the addresses you copied from Sophos Central.
Note
We recommend you don't add any other DNS server in DNS 3. If the firewall switches to the third DNS server, you'll lose the protection offered by DNS Protection.
-
Click Apply.
Configure Sophos Firewall to route local DNS traffic
DNS Protection doesn't resolve local DNS requests. So, if you're using an internal DNS server to resolve local DNS requests, you must add a DNS request route in the firewall. In the DNS request route, specify the local domain and internal DNS server.
To configure Sophos Firewall to route local DNS traffic, do as follows:
- In Sophos Firewall, go to Network > DNS.
- Scroll to DNS request route and click Add.
- In Host/Domain name, enter the local domain.
- In Target servers, select the internal DNS server.
- Click Save.
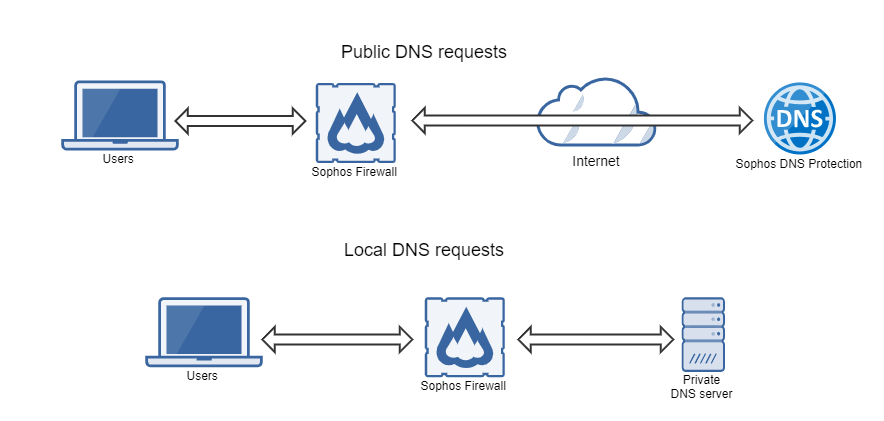
Here's how the firewall routes DNS requests with DNS Protection:
With Sophos Firewall, DNS requests are resolved as follows:
- All requests go from the users to the firewall.
- The firewall forwards local requests to an internal DNS server based on the domain.
- The firewall forwards public DNS requests to DNS Protection.
- The firewall forwards the responses from all DNS requests back to the users.