MITRE ATT&CK
What is MITRE ATT&CK?
MITRE ATT&CK is a globally accessible knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations of cyberattacks. They’re displayed in matrices that are arranged by attack stages, from initial system access to data theft or machine control.
ATT&CK stands for adversarial tactics, techniques, and common knowledge. Tactics are the why of an attack technique. Techniques represent how an adversary achieves a tactical objective by performing an action. Common knowledge is the documented use of tactics and techniques by adversaries.
Framework Definitions
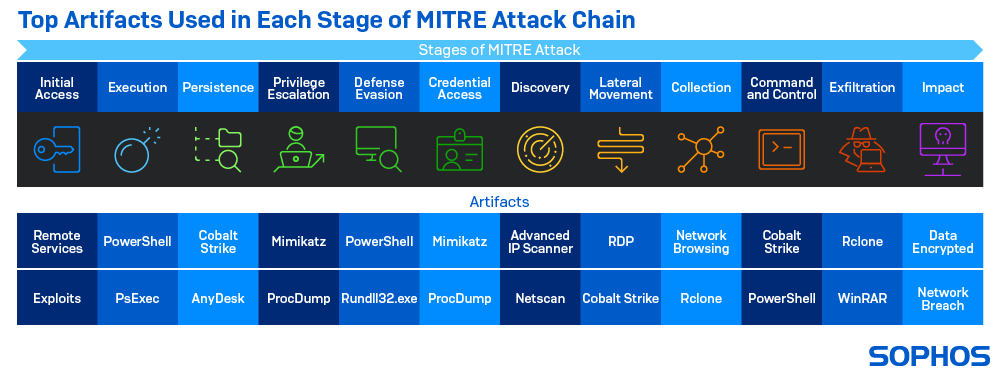
- Initial access: The adversary is trying to get into your network through targeted spear phishing and exploiting weaknesses on public-facing web servers
- Execution: The adversary is trying to run malicious code on a local or remote system to achieve broader goals, like exploring a network or stealing data
- Persistence: The adversary is trying to maintain their foothold across restarts, changed credentials, and other interruptions that could cut off their access
- Privilege escalation: The adversary is trying to gain higher-level permissions on a system or network by taking advantage of system weaknesses, misconfigurations, and vulnerabilities
- Defense Evasion: The adversary is trying to avoid being detected by uninstalling/disabling security software or obfuscating/encrypting data and scripts
- Credential Access: The adversary is trying to steal account names and passwords to gain access to systems, making them much harder to detect
- Discovery: The adversary is trying to figure out your environment by gaining knowledge about the system and internal network
- Lateral Movement: The adversary is trying to move through your environment to find their target and subsequently gain access to it
- Collection: The adversary is trying to gather data of interest to their goal
- Command and Control: The adversary is trying to communicate with compromised systems to control them
- Exfiltration: The adversary is trying to steal data from your network, often packaging it to avoid detection while removing it
- Impact: The adversary is trying to manipulate, interrupt, or destroy your systems and data to disrupt availability or compromise integrity by manipulating business and operational processes
For more on the MITRE ATT&CK framework, visit https://attack.mitre.org/.
Connecting Alert Data and MITRE ATT&CK
As soon as Sophos MDR is enabled on a device (whether it’s an endpoint or server) or an integration is added, data is continuously collected and analyzed in the MDR platform. By analyzing the data and aligning to the MITRE framework, MDR Ops team has a standardized way of categorizing the data into Techniques and Tactics and can more easily conclude how an attacker is exploiting software vulnerabilities in client applications.
Firewalls monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, based on an organization’s previously established security policies.
Example Detections
- Apache Log4j logging remote code execution attempt
- MALWARE-CNC Win.Trojan.Mirage outbound connection
- ELECTRICFISH Command and Control traffic detection
- Nette code injection vulnerability
Example Threat Hunting Discoveries
- Excessive denies - Malicious communication attempts and discover misconfigured device
- Malware beaconing - Hosts beaconing back to a command and control (C2) server
- Internal ICMP scanning - Malicious actors attempting to scan and map a target’s network environment
Three MITRE Tactics discoverable with firewall data
- C2 - Adversary is trying to communicate with compromised systems to control them
- Initial Access - Adversary is trying to get into your network
- Credential Access - Adversary is trying to steal account names and passwords
Public cloud security tools provide security and compliance for cloud services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Kubernetes.
Example Detections
- Impact: EC2/BitcoinDomainRequest.Reputation
- Backdoor: EC2/C2 activity
- Discovery: S3/MaliciousIPCaller
- Dangling DNS record for an app service resource detected
Example Threat Hunting Discoveries
- Cloud environment hardening – Identify assets that need updating, ports which need closing and/or enforce MFA
- Hunt for malicious or unusual behaviour - Identify change of permissions, or actions that a user has never done before outside of usual working hours, admin ports being exposed to internet (e.g. RDP/SSH)
Three MITRE Tactics discoverable with cloud data
- Persistence - Adversary is trying to maintain their foothold
- Privilege Escalation - Adversary is trying to gain higher-level permissions
- Credential Access - Adversary is trying to steal account names and passwords
Email security tools provide threat protection against phishing, malicious URLs, DLP, and attachment scanning.
Example Detections
- Malware campaign detected in SharePoint and OneDrive
- Elevation of Exchange admin privilege
- User accessed link in ZAP-quarantined email
- Unsafe email attachment
Example Threat Hunting Discoveries
- End users clicked suspicious links
- Phishing artifacts were left behind
- An endpoint blocked an executable after an email attachment was opened
- Unexpected email addresses were added to forwarding settings
Three MITRE Tactics discoverable with email data
- Initial Access - Adversary is trying to get into your network
- Impact - Adversary is trying to gain higher-level permissions
- Execution - Adversary is trying to run malicious code
Identity Access Management (IAM) tools manage digital identities and user access to data, systems, and resources within an organization.
Example Detections
- Failed login
- Privilege escalation - First time utilizing a privilege
- Domain policy changes
- First time remote access on host
Example Threat Hunting Discoveries
- Rate of errors in login flow - Surge in number of errors for incorrect username or password as this could indicate credential stuffing
- Rate of attack protection events - Abnormally high traffic for attack protection events such as breached password detection or brute-force attacks for multiple accounts
Three MITRE Tactics discoverable with identity data
- Credential Access - Adversary is trying to steal account names and passwords
- Defense Evasion - The adversary is trying to avoid being detected
- Privilege Escalation - The adversary is trying to gain higher-level permissions
Network security tools typically adopt a combination of data analytics and machine learning to detect anomalies in network traffic flow to protect the corporate network against threats.
Example Detections
- Backdoor: Mirai.Botnet
- CVE-2014-6278 - SHELLSHOCK HTTP Exploit
- SaaS resources deleted
- Executes commands or uses API to obtain system information
Example Threat Hunting Discoveries
- Correlate network data - With process info to detect data staging activity such as archiving files
- Trending campaigns - Detect zero-day exploitation campaigns such as log4j
- Discover dark entities/unmanaged devices - Find devices with no EDR protection
- Domain Generation Algorithm detection - Identify sources in communication with DGA servers
Three MITRE Tactics discoverable with network data
- C2 - Adversary is trying to communicate with compromised systems to control them
- Discovery - Adversary is trying to figure out your environment
- Exfiltration - The adversary is trying to steal data